Six Sigma
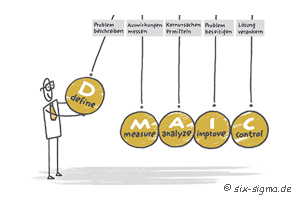
The Six Sigma definition
The Greek letter “Sigma” mathematically represents the standard deviation of a population. Therefor is Sigma the indicator for the deviation from the statistical mean. Six Sigma seeks to methodologically make the performance of processes measurable using key figures. If there is a broad distribution indicating poor process capability, so you can analyse and determine with Six Sigma the cause and effect relationship indicating the specific process problem.
The systematic 5 phase model describes the logical approach for solving problems. This DMAIC cycle is only the beginning of an improvement approach. On the long run the organization achieves a new mindset and view over their processes. The goal is to establishing this mindset and workflow in organizations through a deployment.
The 5 Phases of the Six Sigma improvement process
(short: DMAIC Cycle)

What exactly is the problem, how big is it and what is our goal?

Which process outcomes are involved and what performance is available?

What are the (significant) core reasons for the problem (causal chain)?

How can I solve the problem?

How can the sustainability be assured (organizational anchoring)?
This method derives from W. Deming classic PDCA (Plan / Do / Check / Act). Structuring on this method there are numerous tools (like the 7×7 toolbox) that help to identify and document problems in actual processes, make them measurable and analyzable.
Six Sigma Roles
The Six Sigma hierarchy in an organization provides for the persons involved improvement projects different roles. The names are based on terminology of the martial arts and are titled as “Belts”

Six Sigma Yellow Belt support the Green and Black Belts in their projects. They are usually experts in their processes and contribute with key know-how.

Six Sigma Green Belt manage improvement projects in their own responsibility area.

Six Sigma Black Belt manage complex improvement projects and teams, usually more comprehensive processes.

The Six Sigma Master Black Belt has a leading role in the Six Sigma organization.

The Six Sigma Champion, also called “sponsors” are the project owners, usually from the Management level are responsible for the project and its resources. They drive the projects on.
Our trainings:
Your contact








Find here our customers` testimonials




